-
Filtration
-
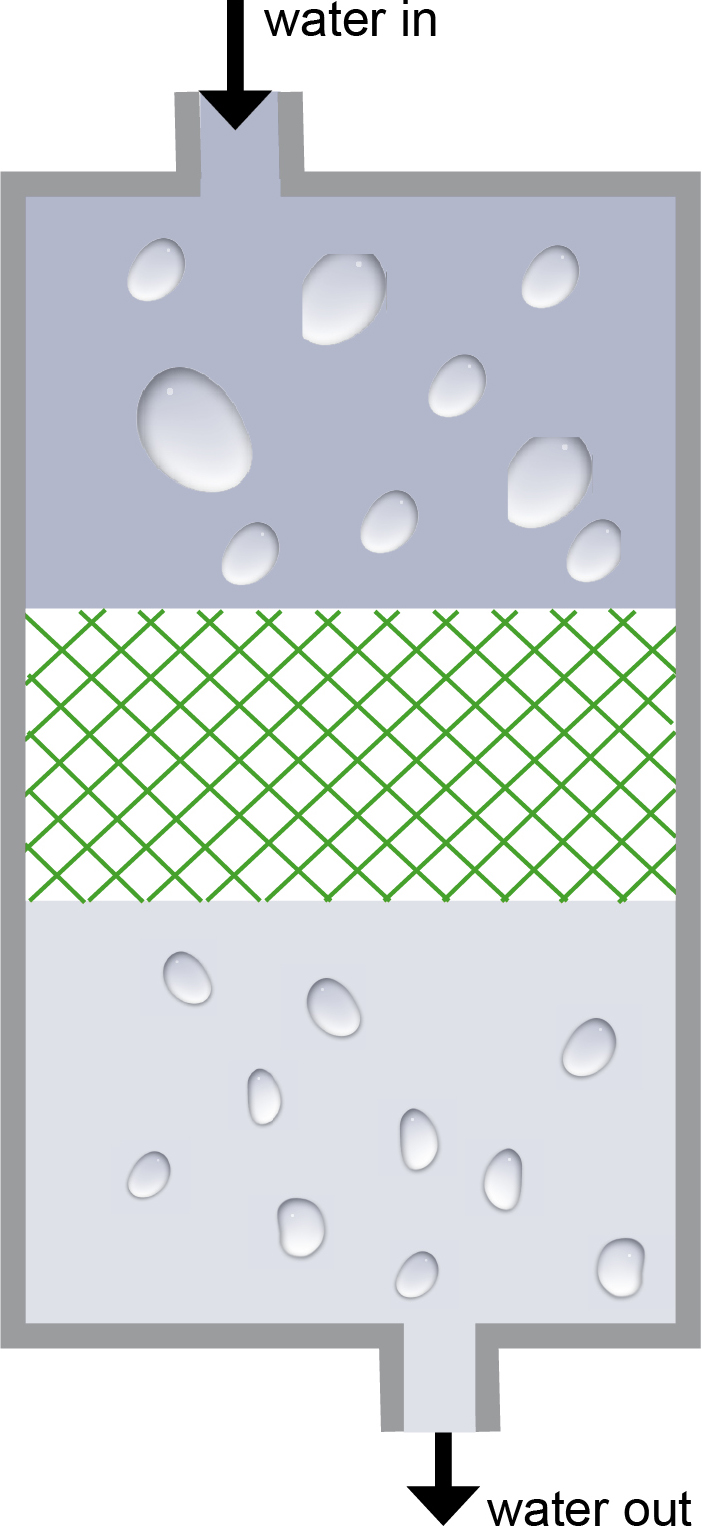 Principle:
Filtering is a mechanical separation process for parting a suspension into its
constituent solid and liquid. For example Silica sand is used as filter material.
Particular importance is attached to activated carbon. Depending on the flow velocity
of water in the filter we distinguish between
slow filters (usually 0.1 to 0.2 m/h) and quick filters (for example 15 m/h).
Principle:
Filtering is a mechanical separation process for parting a suspension into its
constituent solid and liquid. For example Silica sand is used as filter material.
Particular importance is attached to activated carbon. Depending on the flow velocity
of water in the filter we distinguish between
slow filters (usually 0.1 to 0.2 m/h) and quick filters (for example 15 m/h).
-
Due to their large area requirements slow filters are rarely built. Quick filters are available
with open ponds or closed tanks. For cleaning they are purged it with clean water and/or
air. To increase the effect of space and to extend the duration between two purgings
quick filters often to be quick filter often run as multi-layer filters. For example with
two-layer-filters, the upper layer consists of a lighter material with coarser grain size
(for example filter carbon, expanded clay, expanded shale or pumice) and the bottom layer
of a heavier material finer grain size (usually quartz sand).
 Principle:
Filtering is a mechanical separation process for parting a suspension into its
constituent solid and liquid. For example Silica sand is used as filter material.
Particular importance is attached to activated carbon. Depending on the flow velocity
of water in the filter we distinguish between
slow filters (usually 0.1 to 0.2 m/h) and quick filters (for example 15 m/h).
Principle:
Filtering is a mechanical separation process for parting a suspension into its
constituent solid and liquid. For example Silica sand is used as filter material.
Particular importance is attached to activated carbon. Depending on the flow velocity
of water in the filter we distinguish between
slow filters (usually 0.1 to 0.2 m/h) and quick filters (for example 15 m/h).


